BATTERY
POWER BACKUP SERIES
BATTERY
POWER BACKUP SERIES


| Battery Parameters | Tubular |
|---|---|
| Reliability | Most reliable |
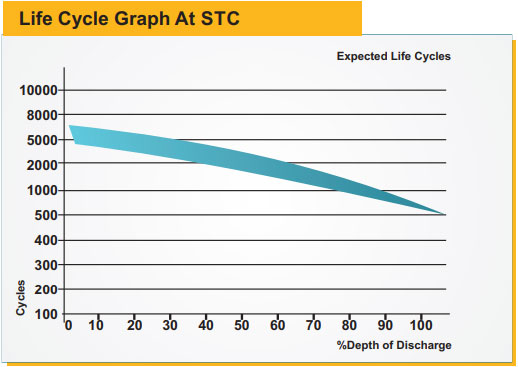
| Charge Cycles | 1100-1500 |
| Electrolyte Stratification Risk | Low |
| Thermal Management | High |
| Interface Surface Area | High |
| Electrical Resistance | Low |
Automotive (SLI – Starting Lighting Ignition), electrical vehicles, golf carts, hybrid vehicles, motive power (traction), standby emergency power backup for telephone exchange, stationery (UPS & Inverter), emergency lighting.

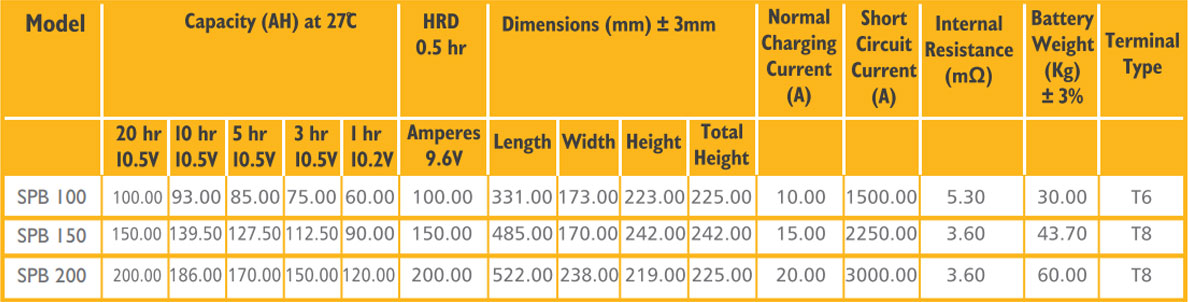
| Model | Big Warrior Series | |||
| Battery rating | 100 Ah @C20 |
150 Ah @C20 | 200 Ah @C20 | 225 Ah @C20 |
| Type of Battery | Tubular | |||
| Model Offered | SBW 100 | SBW 150 | SBW 200 | SBW 225 |
| Nominal Voltage | 12V | |||
| Number of cell | 6 | |||
| Shelf life | 6 years | |||
| Nominal Capacity(27°C) | ||||
| Cell Capacity @ C20 | 102 Ah | 153 Ah | 200 Ah | 225 Ah |
| Cell Capacity @ C10 | 81 Ah | 120 Ah | 176 Ah | 200 Ah |
| Cell Capacity @ C3 | 57.5 Ah | 86 Ah | 126 Ah | 165 Ah |
| AH Efficiency | > 90% | |||
| WH Efficiency | > 80% | |||
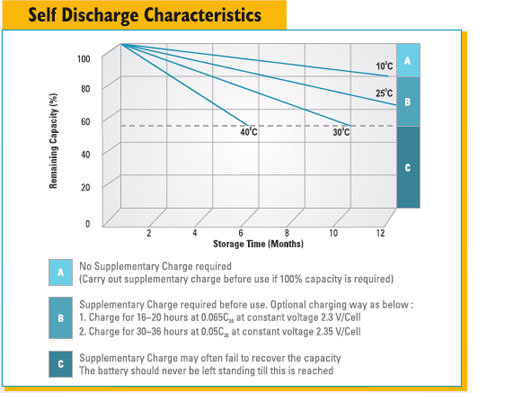
| Recommended max. period of storage | 3 months at 27°C | |||
| Grid Alloy | Lead Antimony alloy | |||
| Container & Lid Material | PPCP | |||
| Sealing Method | Heat Sealing | |||
| Plate type | Tubular Pos. & Flat Neg. | |||
| Separator | Polyethylene | |||
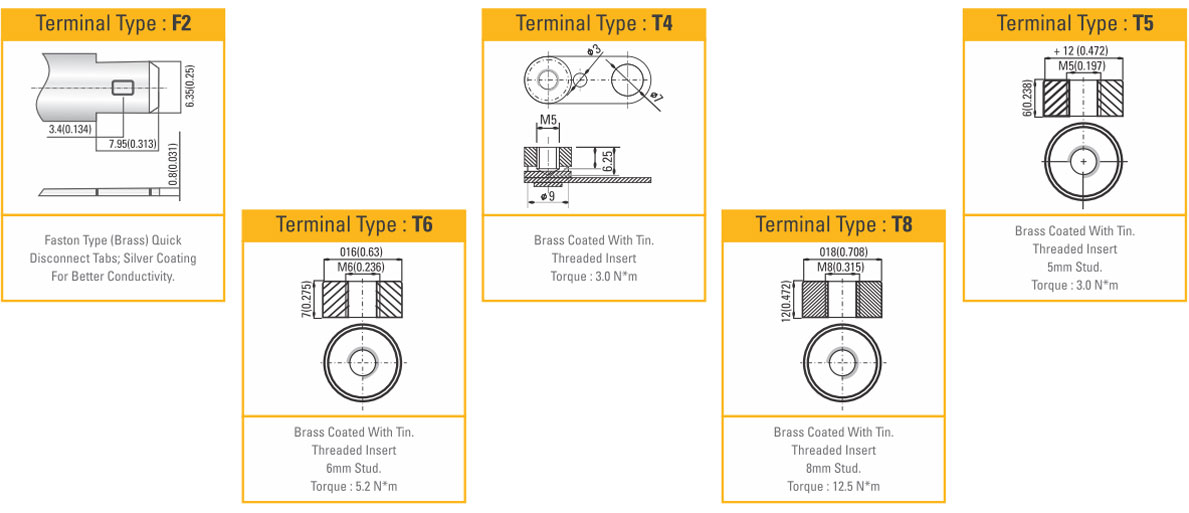
| Terminals & ICC | Bolted type terminals with lead coated fastners | |||
| Mounting | Vertical | |||
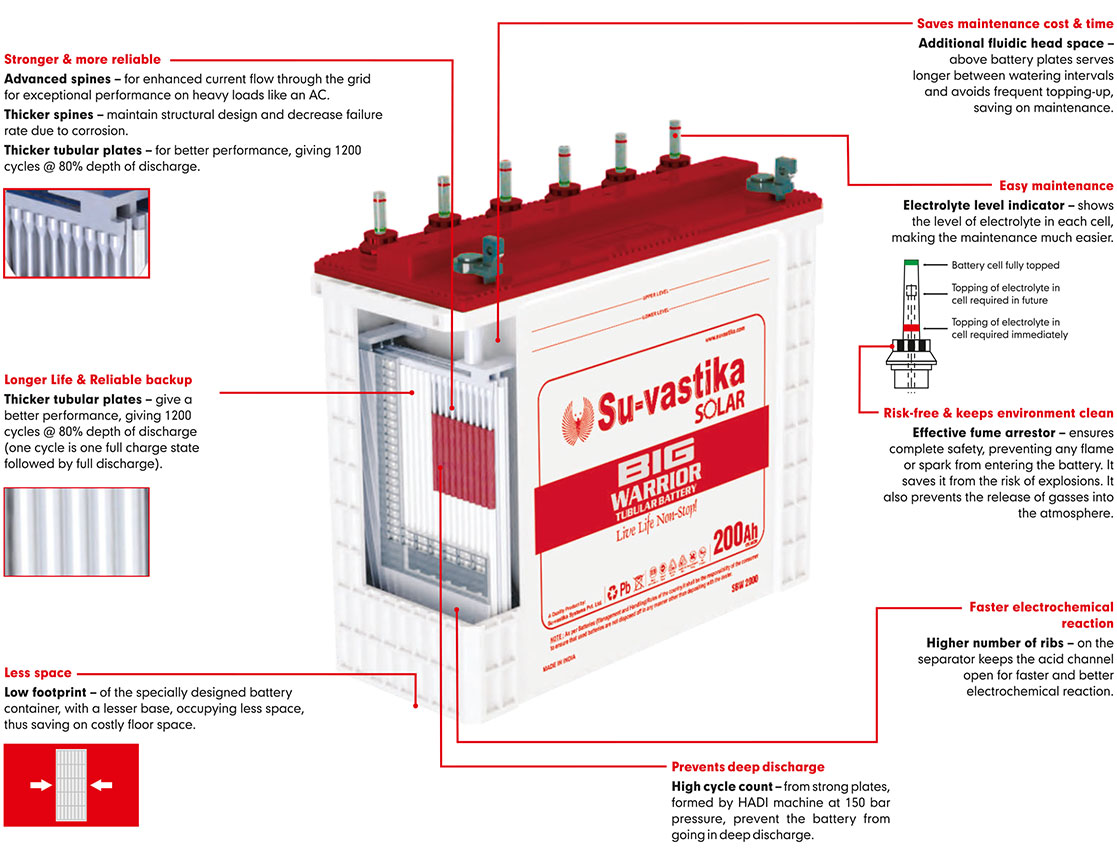
| Acid Level Indicators | Provided | |||
| Provided | Factory charged | |||
| Self Discharge at 27°C (average) Operating Temp. range |
2.5% | 3% | ||
| Discharge | -20~ 50°C | |||
| Charge | -10~ 50°C | |||
| Storage | -20~ 50°C | |||
| Max. Discharge Current 77°F (25°C) | 100 A (3 sec) | 450A(3 sec) | 600A(3 sec) | 675A(3 sec) |
| Short Circuit Current | 100 A | 150 A | 200 A | 225 A |
| Cycle Use | 14.2 - 14.5 V | 14.4 - 14.7 | 14.4 - 14.7 | 14.4 - 14.7 |
| Maximum charging Current 10% of Capacity | 10 Amp | 15 Amp | 20 Amp | 23 Amp |
| Temperature compensation | 75mV/300moh | |||
| Weight (Kg) Gross +/- 3% | 52 | 57.5 | 64 | 68 |
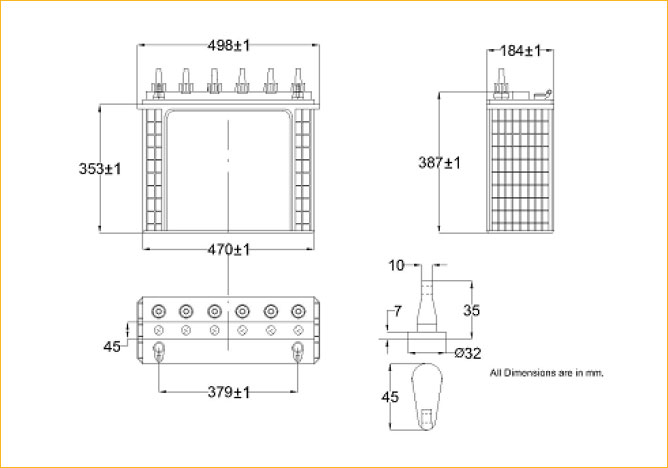
| Dimensions (L x W x H )in mm | 505 x 187 x 394 | |||
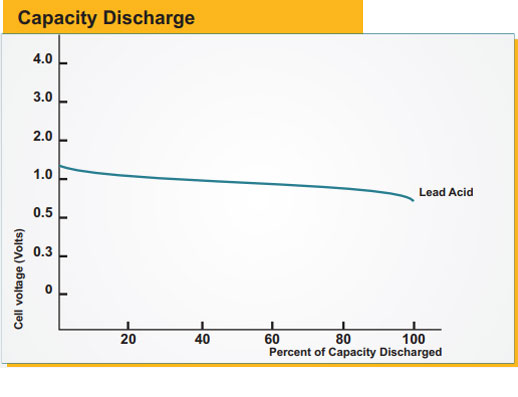
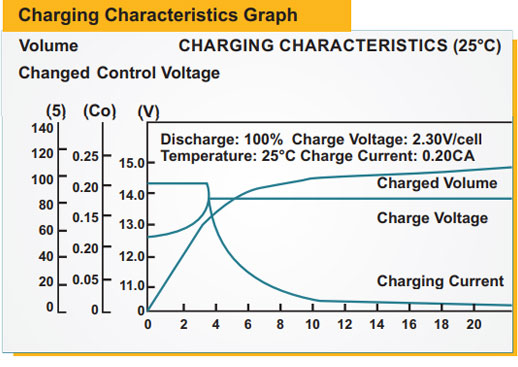
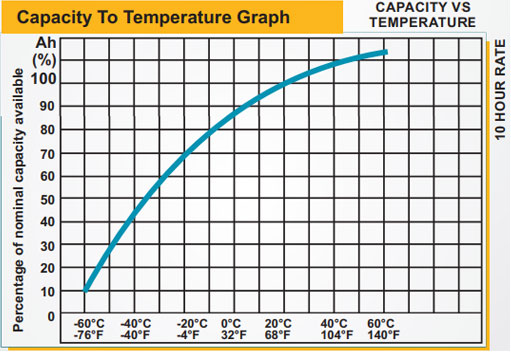
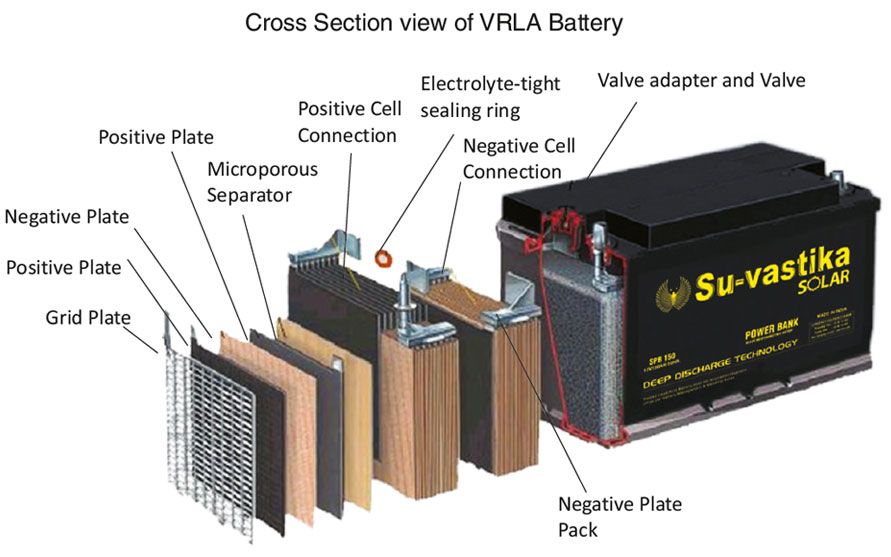
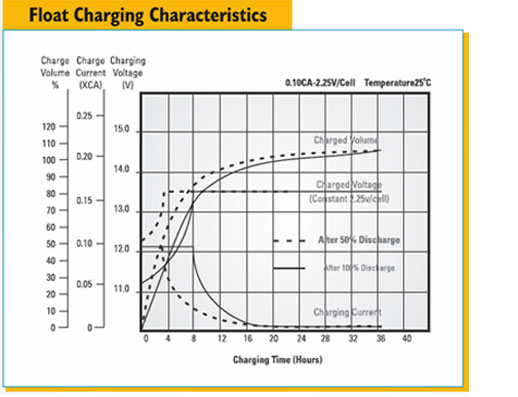
All lead-acid batteries release hydrogen from the negative plate and oxygen from the positive plate during charging. VRLA batteries have
one-way, pressure-relief valves. Without the ability to retain pressure within the cells, hydrogen and oxygen would be lost to the
atmosphere, eventually drying out the electrolyte and separators.
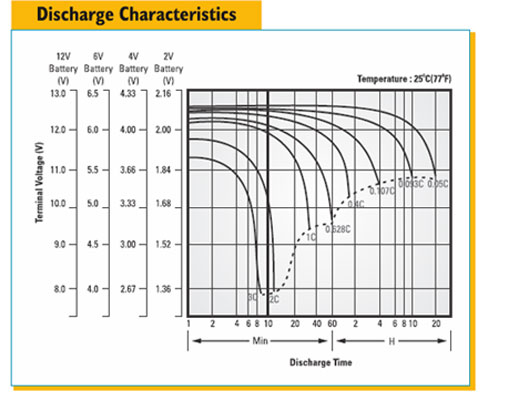
Voltage is electrical pressure (energy per unit of charge). Charge (ampere-hours) is a quantity of electricity. Current (amperes) is electrical
flow (charging speed). A battery can only store a certain quantity of electricity. The closer it gets to being fully charged, the slower it must be
charged.
Temperature also affects charging. If the right voltage is used for the temperature, a battery will accept charge at its ideal rate. If too much
voltage is used, charge will be forced through the battery faster than it can be stored.
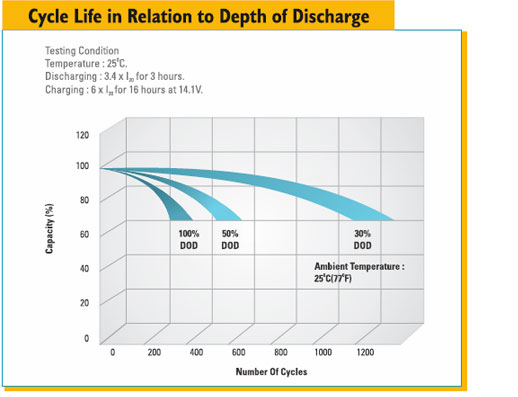
The major application of the VRLA battery is used in emergency lighting or uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) for individual computers or work stations to high-power UPS in telecommunications facilities. A continuous supply of power is also critical in areas such as banking, stock exchanges, hospitals, air traffic control centers etc. where brief interruptions pose the risk of loss of critical data or hazards to health and safety.
Su-vastika has come up with their latest power bank series of Sealed Maintenance Free (SMF) batteries that are specially designed for optimum performance, very long life and high reliability. These are eminently suitable for a wide range of applications. SMF batteries do not emit corrosive gases and are leak proof. They have stable and reliable capacity. SMF batteries guarantee a long service life in standby or cyclic service. The computer-aided design and the manufacturing expertise of Su-vastika, ensure the best quality products in the industry. Su-vastika’s SMF batteries are the perfect match for your inverter or UPS; they can perform under extreme conditions and can withstand deep discharge and overcharge as well.